Synantropní vegetace
Synantropizace krajiny
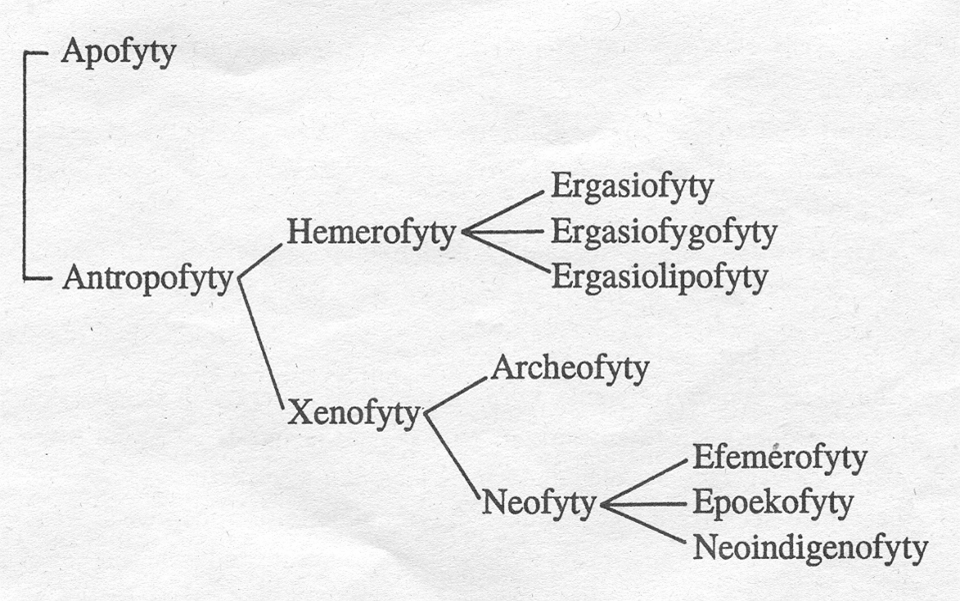
synantropní, ruderální, segetální, apofytizace – apofyta (303 v ČR)
rostliny cizího původu (antropofyta, aliens, exotics, nonindigenous species) - 1378, tj. 33,4% flóry ČR (2754 domácích)
archeofyta (332, tj 24.1%) vs. neofyta (1046, tj. 75.9%), invazní (90, tj. 6.6% neofytů), naturalizované (397) a příležitostné (891), 22 archeofytů je v červeném seznamu
formování společenstev: historie, geografický původ, kvalitativně nové substráty
určující faktory prostředí: disturbance, sucho, teplo, živiny
historie výzkumu
složitost popisu: inflace jednotek, deduktivní metoda, klasifikace dle dominant
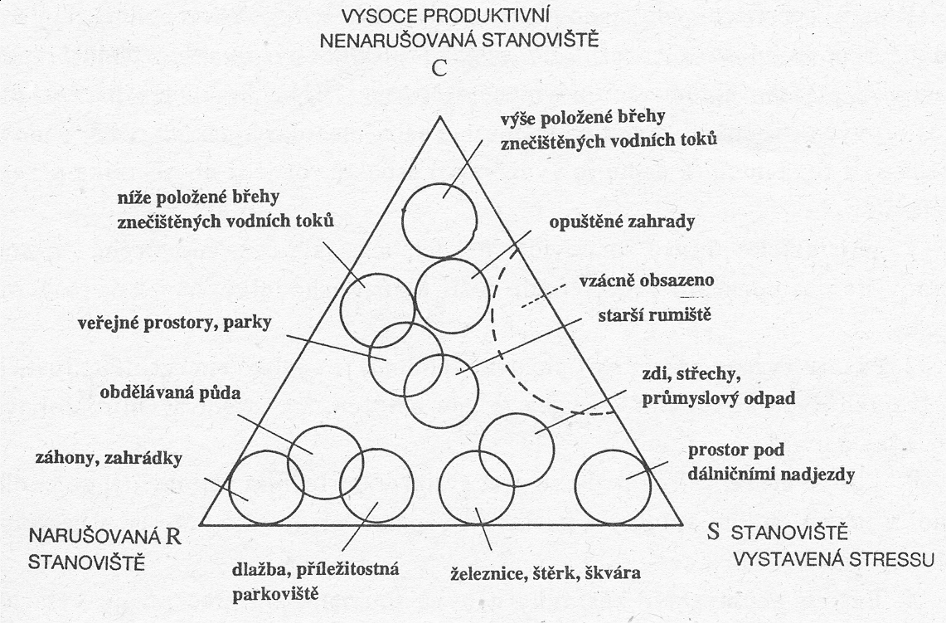
Parametry klasifikace:
doba zavlečení
úmyslně, neúmyslně
stupeň naturalizace - ve společenstvech ruderálních x přirozených
Proantroofyty - původní druhy
Synantropofyty - synantropní rostliny
nejúspěšnější apofyta
Calamagrostis epigeios, Urtica dioica, Calamagrostis villosa, Epilobium angustifolium, Artemisia vulgaris, Phalaris arundinacea, Phragmites australis, Agropyron repens
+ dřeviny: Betula pendula, Fraxinus excelsior, Salix caprea, Sambucus nigra
hodně se kryje s druhy nejúspěšnějšími v sukcesi (15 studovaných sérií): Calamagrostis epigeios, Artemisia vulgaris, Chenopodium album, Arrhenatherum elatius, Agropyron repens, Betula pendula, Phalaris arundinacea, Calamagrostis villosa, Deschampsia flexuosa, Sambucus nigra
„ideální“ apofyt
vysoký, větrosprašný oddenkový geofyt nebo hemikryptofyt, produkující značné množství snadno šiřitelných diaspor, se schopností intenzivního bočního rozrůstání, vyžadující vyšší množství živin a dostatečnou vlhkost
nejúspěšnější neofyta:
invaze do polopřirozených a člověkem vytvořených stanovišť
Epilobium adenocaulon, Juncus tenuis, Reynoutria japonica, Solidago canadensis, Impatiens parviflora, I. glandulifera, Bidens frondosa, Heracleum mantegazzianum, Robinia pseudacacia, Trifolium hybridum, Amaranthus retroflexus, Cardaria draba, Chamomilla suaveolens, Conyza canadensis, Galinsoga ciliata, G. parviflora, Veronica persica
„ideální“ invazní druh:
na (polo)přirozených stanovištích: vysoký, vytrvalý geofyt nebo hemikryptofyt (případně dřevina), s C-strategií, většinou pěstovaný jako okrasná rostlina - na (polo)přirozených stanovištích
na člověkem vytvořených stanovištích: terofyt (výjimečně geofyt), CR-stratég, většinou zavlečen neúmyslně
Ruderal species
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia

A ruderal species is a plant species that is first to colonise disturbed lands. The disturbance may be natural (e.g., wildfires or avalanches), or man-made - constructional (e.g., road construction, building construction or mining), or agricultural (e.g., abandoned farming fields or abandoned irrigation ditches).
Ruderal species typically dominate the disturbed area for a few years, gradually losing the competition to other native species. However, in extreme disturbance circumstances, such as when the natural topsoil is covered with a foreign substance, a single-species ruderal community may become permanently established, as depicted in the image on the right. In addition, some ruderal invasive species may have such a competitive advantage over the natural species that they, too, may permanently prevent a disturbed area from returning to its original state despite natural topsoil.
Features
Features contributing to a species success as ruderal are:
- Massive seed production
- Modest seedling nutritional requirements
- Fast-growing roots
- Independence of mycorrhizae
See also

- Edge effect
- Restoration ecology
- Example ruderal species:
References and external links
- "Ruderal Community" on the California Polytechnic State University web site
- St. John TV. 1987. SOIL DISTURBANCE AND THE MINERAL NUTRITION OF NATIVE PIANTS in Proceedings of the 2nd Native Plant Revegetation Symposium
- Chapin. FS. III. 1980. The mineral nutrition of wild plants. Ann. Rev. Ecol. System, 11:233-260.
- Ruderal in the 1911 Britannica
Tento článek je licencován podGNU Free Documentation Licence. Používá materiál zčlánek"ruderal".